Question 1:
Sides of triangles are given below. Determine which of them are right triangles? In case of a right triangle, write the length of its hypotenuse.
(i) 7 cm, 24 cm, 25 cm
(ii) 3 cm, 8 cm, 6 cm
(iii) 50 cm, 80 cm, 100 cm
(iv) 13 cm, 12 cm, 5 cm
(i) It is given that the sides of the triangle are 7 cm, 24 cm, and 25 cm.
Squaring the lengths of these sides, we will obtain 49, 576, and 625.
49 + 576 = 625
Or,
The sides of the given triangle are satisfying Pythagoras theorem.
Therefore, it is a right triangle.
We know that the longest side of a right triangle is the hypotenuse.
Therefore, the length of the hypotenuse of this triangle is 25 cm.
(ii) It is given that the sides of the triangle are 3 cm, 8 cm, and 6 cm.
Squaring the lengths of these sides, we will obtain 9, 64, and 36.
However, 9 + 36 ≠ 64
Or, 32 + 62 ≠ 82
Clearly, the sum of the squares of the lengths of two sides is not equal to the square of the length of the third side.
Therefore, the given triangle is not satisfying Pythagoras theorem.
Hence, it is not a right triangle.
(iii)Given that sides are 50 cm, 80 cm, and 100 cm.
Squaring the lengths of these sides, we will obtain 2500, 6400, and 10000.
However, 2500 + 6400 ≠ 10000
Or, 502 + 802 ≠ 1002
Clearly, the sum of the squares of the lengths of two sides is not equal to the square of the length of the third side.
Therefore, the given triangle is not satisfying Pythagoras theorem.
Hence, it is not a right triangle.
(iv)Given that sides are 13 cm, 12 cm, and 5 cm.
Squaring the lengths of these sides, we will obtain 169, 144, and 25.
Clearly, 144 +25 = 169
Or,
The sides of the given triangle are satisfying Pythagoras theorem.
Therefore, it is a right triangle.
We know that the longest side of a right triangle is the hypotenuse.
Therefore, the length of the hypotenuse of this triangle is 13 cm.
Squaring the lengths of these sides, we will obtain 49, 576, and 625.
49 + 576 = 625
Or,
The sides of the given triangle are satisfying Pythagoras theorem.
Therefore, it is a right triangle.
We know that the longest side of a right triangle is the hypotenuse.
Therefore, the length of the hypotenuse of this triangle is 25 cm.
(ii) It is given that the sides of the triangle are 3 cm, 8 cm, and 6 cm.
Squaring the lengths of these sides, we will obtain 9, 64, and 36.
However, 9 + 36 ≠ 64
Or, 32 + 62 ≠ 82
Clearly, the sum of the squares of the lengths of two sides is not equal to the square of the length of the third side.
Therefore, the given triangle is not satisfying Pythagoras theorem.
Hence, it is not a right triangle.
(iii)Given that sides are 50 cm, 80 cm, and 100 cm.
Squaring the lengths of these sides, we will obtain 2500, 6400, and 10000.
However, 2500 + 6400 ≠ 10000
Or, 502 + 802 ≠ 1002
Clearly, the sum of the squares of the lengths of two sides is not equal to the square of the length of the third side.
Therefore, the given triangle is not satisfying Pythagoras theorem.
Hence, it is not a right triangle.
(iv)Given that sides are 13 cm, 12 cm, and 5 cm.
Squaring the lengths of these sides, we will obtain 169, 144, and 25.
Clearly, 144 +25 = 169
Or,
The sides of the given triangle are satisfying Pythagoras theorem.
Therefore, it is a right triangle.
We know that the longest side of a right triangle is the hypotenuse.
Therefore, the length of the hypotenuse of this triangle is 13 cm.
Question 2:
PQR is a triangle right angled at P and M is a point on QR such that PM ⊥ QR. Show that PM2 = QM × MR.
Question 3:
In the following figure, ABD is a triangle right angled at A and AC ⊥ BD. Show that
(i) AB2 = BC × BD
(ii) AC2 = BC × DC
Question 4:
Given that ΔABC is an isosceles triangle.
∴ AC = CB
Applying Pythagoras theorem in ΔABC (i.e., right-angled at point C), we obtain
Question 5:
ABC is an isosceles triangle with AC = BC. If AB2 = 2 AC2, prove that ABC is a right triangle.
Given that,
Question 6:
ABC is an equilateral triangle of side 2a. Find each of its altitudes.
Let AD be the altitude in the given equilateral triangle, ΔABC.
We know that altitude bisects the opposite side.
∴ BD = DC =
In an equilateral triangle, all the altitudes are equal in length.
Therefore, the length of each altitude will be.
Question 7:
Prove that the sum of the squares of the sides of rhombus is equal to the sum of the squares of its diagonals.
In ΔAOB, ΔBOC, ΔCOD, ΔAOD,
Applying Pythagoras theorem, we obtain
Question 8:
In the following figure, O is a point in the interior of a triangle ABC, OD ⊥ BC, OE ⊥ AC and OF ⊥ AB. Show that
Let OA be the wall and AB be the ladder.
Therefore, by Pythagoras theorem,
Therefore, the distance of the foot of the ladder from the base of the wall is
6 m.
Let OB be the pole and AB be the wire.
By Pythagoras theorem,
Therefore, the distance from the base is
m .
Let CD and AB be the poles of height 11 m and 6 m.
Therefore, CP = 11 − 6 = 5 m
From the figure, it can be observed that AP = 12m
Applying Pythagoras theorem for ΔAPC, we obtain
Therefore, the distance between their tops is 13 m.
Applying Pythagoras theorem in ΔACE, we obtain
Let the side of the equilateral triangle be a, and AE be the altitude of ΔABC.
∴ BE = EC =BC/2 =a/2
Applying Pythagoras theorem in ΔABE, we obtain
AB2 = AE2 + BE2
4AE2 = 3a2
⇒ 4 × (Square of altitude) = 3 × (Square of one side)
Given that, AB =
cm, AC = 12 cm, and BC = 6 cm
It can be observed that
AB2 = 108
AC2 = 144
And, BC2 = 36
AB2 +BC2 = AC2
The given triangle, ΔABC, is satisfying Pythagoras theorem.
Therefore, the triangle is a right triangle, right-angled at B.
∴ ∠B = 90°
Hence, the correct answer is (C).
(i) OA2 + OB2 + OC2 − OD2 − OE2 − OF2 = AF2 + BD2 + CE2
(ii) AF2 + BD2 + CE2 = AE2 + CD2 + BF2
Join OA, OB, and OC.
(i) Applying Pythagoras theorem in ΔAOF, we obtain
Similarly, in ΔBOD,
OB2 = OD2 + BD2
Similarly, in ΔCOE,
(ii) From the above result,
(i) Applying Pythagoras theorem in ΔAOF, we obtain
Similarly, in ΔBOD,
OB2 = OD2 + BD2
Similarly, in ΔCOE,
(ii) From the above result,
Question 9:
A ladder 10 m long reaches a window 8 m above the ground. Find the distance of the foot of the ladder from base of the wall.
Let OA be the wall and AB be the ladder.
Therefore, by Pythagoras theorem,
Therefore, the distance of the foot of the ladder from the base of the wall is
6 m.
Question 10:
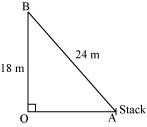
A guy wire attached to a vertical pole of height 18 m is 24 m long and has a stake attached to the other end. How far from the base of the pole should the stake be driven so that the wire will be taut?
Let OB be the pole and AB be the wire.
By Pythagoras theorem,
Therefore, the distance from the base is
m .
Question 12:
Two poles of heights 6 m and 11 m stand on a plane ground. If the distance between the feet of the poles is 12 m, find the distance between their tops.
Let CD and AB be the poles of height 11 m and 6 m.
Therefore, CP = 11 − 6 = 5 m
From the figure, it can be observed that AP = 12m
Applying Pythagoras theorem for ΔAPC, we obtain
Therefore, the distance between their tops is 13 m.
Question 13:
D and E are points on the sides CA and CB respectively of a triangle ABC right angled at C. Prove that AE2 + BD2 = AB2 + DE2
Applying Pythagoras theorem in ΔACE, we obtain
Question 14:
The perpendicular from A on side BC of a ΔABC intersect BC at D such that DB = 3 CD. Prove that 2 AB2 + BC2 = 2 AC
Question 16:
In an equilateral triangle, prove that three times the square of one side is equal to four times the square of one of its altitudes.
Let the side of the equilateral triangle be a, and AE be the altitude of ΔABC.
∴ BE = EC =BC/2 =a/2
Applying Pythagoras theorem in ΔABE, we obtain
AB2 = AE2 + BE2
4AE2 = 3a2
⇒ 4 × (Square of altitude) = 3 × (Square of one side)
Question 17:
The angle B is:
(A) 120° (B) 60°
(C) 90° (D) 45°
Given that, AB =
cm, AC = 12 cm, and BC = 6 cm
It can be observed that
AB2 = 108
AC2 = 144
And, BC2 = 36
AB2 +BC2 = AC2
The given triangle, ΔABC, is satisfying Pythagoras theorem.
Therefore, the triangle is a right triangle, right-angled at B.
∴ ∠B = 90°
Hence, the correct answer is (C).